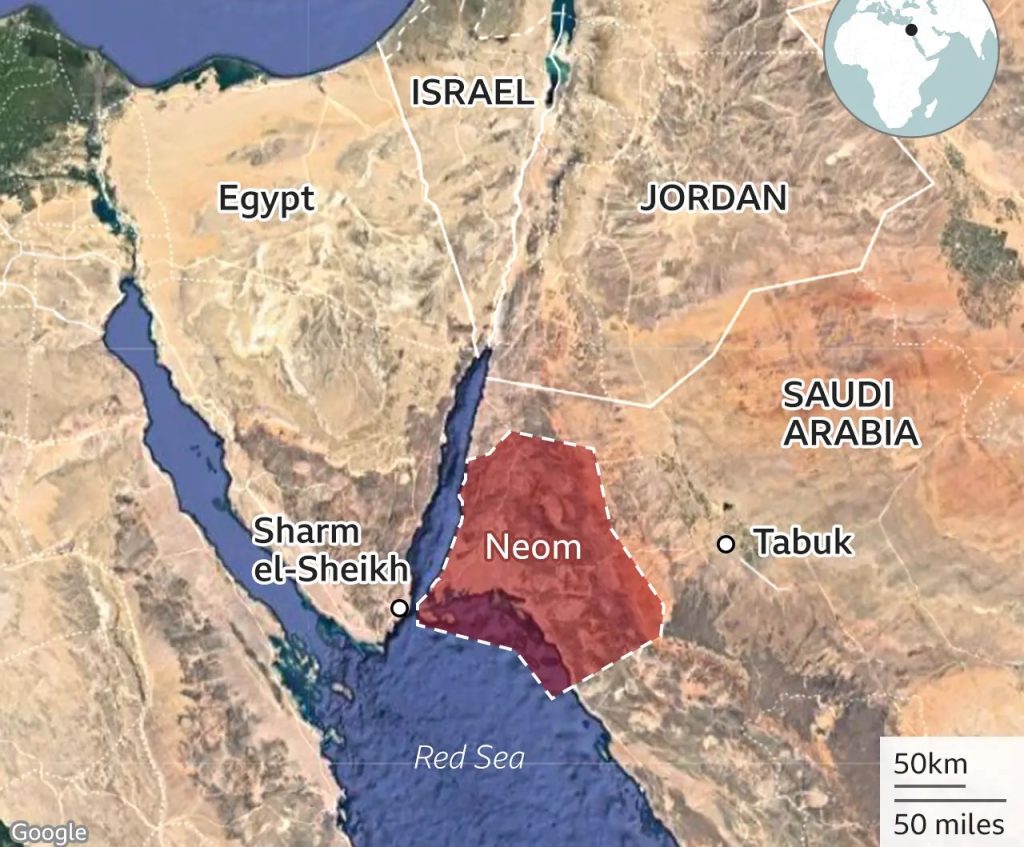
NEOM, Saudi Arabia's ambitious $500 billion megacity project, aims to be a futuristic hub powered by renewable energy, advanced technology, and sustainable living. Envisioned as a flagship initiative under Saudi Vision 2030, NEOM is expected to set new standards for urban development. However, the project faces several significant execution challenges that could impact its progress and ultimate success.
1. Logistical and Infrastructure Challenges
Geographical and Environmental Constraints
- Remote Location: NEOM is located in a remote desert region along the Red Sea, presenting significant logistical challenges in terms of transporting materials, equipment, and workforce.
- Harsh Climate: The extreme desert climate poses additional challenges, including ensuring the well-being of construction workers and the durability of infrastructure in high temperatures and sandy conditions.
Infrastructure Development
- Foundational Infrastructure: Building foundational infrastructure such as roads, water supply systems, and electricity grids from scratch is a massive undertaking. The initial stages of construction are time-consuming and resource-intensive.
- Sustainable Solutions: NEOM’s commitment to sustainability requires innovative solutions for energy, water, and waste management, which may not yet be fully developed or tested on such a large scale.
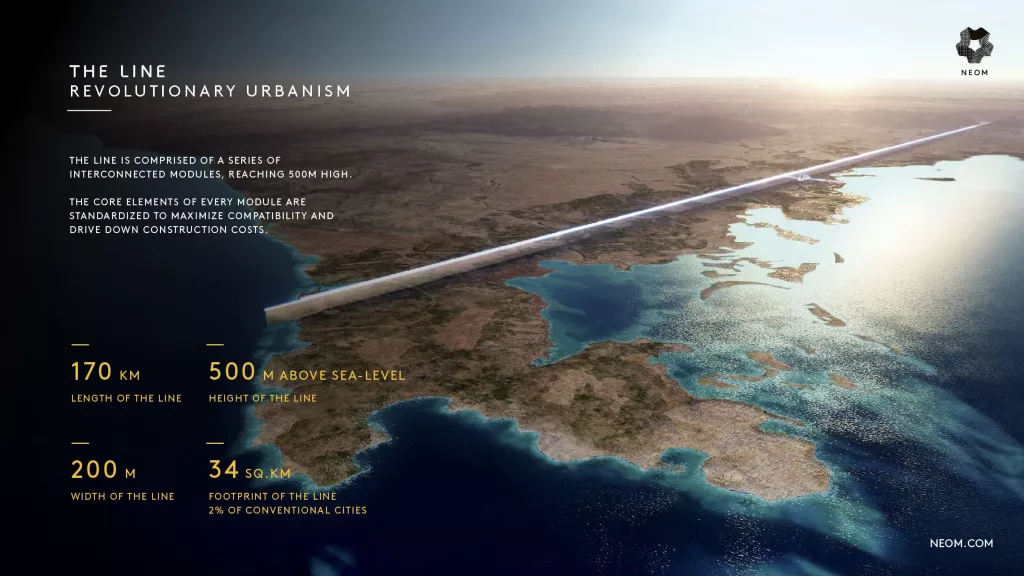
image Source: Neom.com
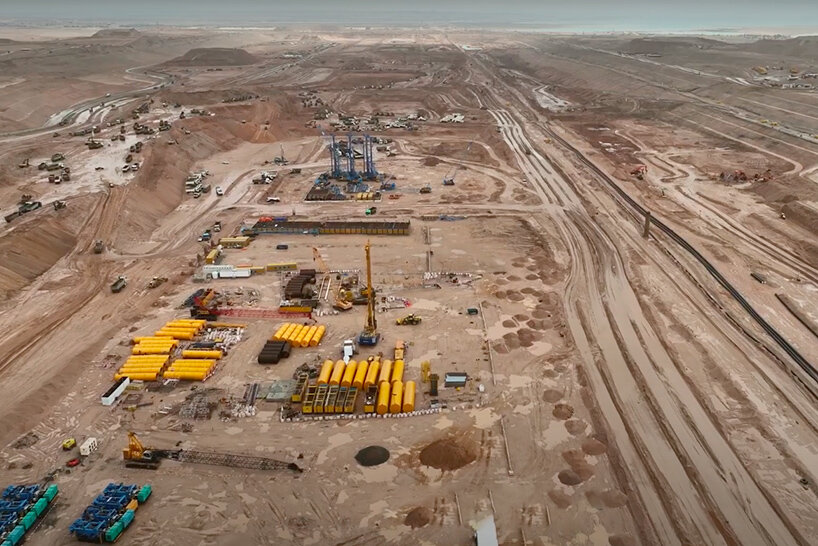

The 100 mile (Approx:170 km) line city that was planned to be completed and operational by 2030 is in progress. But given the funding and project execution challenges the scope has been reduced to just one (1) mile by 2030.
2. Technological Integration
Advanced Technologies
- Emerging Technologies: NEOM plans to integrate cutting-edge technologies such as AI, IoT, and autonomous systems. However, many of these technologies are still in developmental stages and may not be ready for large-scale deployment.
- Interoperability and Integration: Ensuring that various advanced technologies work seamlessly together requires extensive planning, testing, and coordination among tech providers and stakeholders.
Cybersecurity Risks
- Data Privacy and Security: The high level of technological integration raises significant concerns about data privacy and cybersecurity. Protecting sensitive information from cyber threats is a critical challenge.


Image source: Neom.com and Google maps. Oxagon planned versus actual.
3. Financial and Economic Challenges
Budget Management
- Cost Overruns: Large-scale projects like NEOM are prone to cost overruns due to unforeseen challenges, changing project scope, and escalating material and labor costs.
- Economic Viability: Ensuring the economic viability of NEOM involves attracting businesses, residents, and tourists, which requires significant marketing efforts and incentives.
Funding and Investment
- Securing Investment: Despite strong backing from the Saudi government, attracting sufficient private investment is crucial. Investors may be wary of the high risks and long-term nature of the project.
- Economic Diversification: NEOM is part of Saudi Arabia’s broader goal to diversify its economy away from oil dependence. Achieving this requires a balanced and strategic approach to economic development within NEOM.
4. Regulatory and Bureaucratic Hurdles
Legal and Regulatory Framework
- New Regulations: Establishing a new regulatory framework tailored to NEOM’s unique needs is complex. It involves creating laws and regulations that encourage innovation while ensuring safety, security, and fairness.
- Bureaucratic Delays: Navigating Saudi Arabia’s existing bureaucratic processes can lead to delays. Streamlining approvals and permits is essential to maintain the project timeline.
Governance and Policy
- Effective Governance: Implementing effective governance structures that can oversee the project’s development, resolve disputes, and adapt to changing circumstances is a major challenge.
- Policy Adaptation: Policies must be adaptable to accommodate the fast-paced technological advancements and evolving project requirements.
5. Social and Cultural Challenges

Community and Workforce Engagement
- Local Workforce Development: Building a skilled local workforce to support the project’s advanced technological needs requires significant investment in education and training programs.
- Cultural Integration: Balancing the influx of international workers and residents with the local culture and traditions is essential to foster a cohesive and inclusive community.
Public Perception and Support
- Public Relations: Gaining and maintaining public support, both domestically and internationally, is critical. Transparency and effective communication about the project’s progress and benefits are necessary to build trust.
- Human Rights Concerns: Addressing international concerns about human rights practices in Saudi Arabia is important for maintaining positive global perceptions and attracting foreign investment.
Takeaway
NEOM's vision of a futuristic, sustainable megacity is grand and inspiring, but the path to its realization is fraught with significant challenges. I am supportive of the vision and congratulate the project team working day and night for making the project a success. However, the laws of engineering and science drive the actual execution.
Addressing logistical, technological, financial, regulatory, and social hurdles requires meticulous planning, robust governance, and sustained investment. As the project progresses, its ability to adapt to and overcome these challenges will determine its ultimate success and its potential to serve as a model for future urban developments.